- If someone hits his or her head, they should record the date. Any peculiar symptoms that occur even weeks later should be documented. This includes nausea and vomiting. A normal CAT scan 24 hours after getting hit in the head doesn’t mean that bleeding in the brain won’t eventually occur.
- A skull fracture is another type of head injury that can affect the brain. Sometimes with a fracture, pieces of bone can cut into the brain and cause bleeding and other types of injury.
- Symptoms and Causes of Frontal Lobe Brain Damage Treatment of Frontal Lobe Brain Trauma With any type of head trauma treatment and brain injury management, the initial interventions focus on stopping bleeding and managing swelling and nerve death.
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 11, 2019.
- Health Guide
What Is It?
Trauma to the head can cause several types of head and brain injuries, also called traumatic brain injury (TBI). Problems from head injury include:
Closed head injury: To get brain bleeding from a car accident just by accelerate-decelerate motion of the head is possible if the person is on anticoagulant (blood thinner) and have a brain that is less then healthy, such as in cerebral atrophy. Usual sypmtoms are stiff neck and severe headaches.
Skull fracture — A skull fracture is a crack or break in one of the skull's bones. In some cases, the skull is dented inward so that fragments of shattered bone are pressed against the surface of the brain. This is called a depressed skull fracture. In most cases, a skull fracture causes a bruise (contusion) on the surface of the brain under the fracture.
Epidural hematoma — This is a very serious form of bleeding that happens when one of the blood vessels under the skull is torn during an injury. Usually the skull is fractured as well. As the injured vessel bleeds, blood collects in the space between the skull and the dura, the outermost of the three membranes that cover the brain. This collection of blood is called a hematoma. The hematoma can expand within the skull and press on the brain, causing death.
Acute subdural hematoma — In this injury, a blood vessel tears, and blood collects between the dura and the surface of the brain. This can happen when the head is hit or when a sudden stop causes the head to move violently forward and back (whiplash). Acute subdural hematoma develops rapidly, most commonly after serious head trauma caused by an assault, car accident or fall. It is a very severe brain injury that typically causes unconsciousness, and it is fatal in about 50% of cases.
Chronic subdural hematoma — Unlike the acute form, this type of subdural hematoma usually develops gradually because the bleeding inside the skull is less dramatic, and the hematoma can accumulate in several small, separate episodes of bleeding. A chronic subdural hematoma typically follows a fairly minor head injury in a person who is elderly, who is taking blood-thinning medications or whose brain has shrunk as a result of alcoholism or dementia. Symptoms develop gradually over one to six weeks. The most common symptoms are drowsiness, inattentiveness or confusion, headaches, changes in personality, seizures and mild paralysis.
Intraparenchymal hemorrhages and contusions— 'Intraparenchymal' means 'in the tissue.' Intraparenchymal hemorrhage is pooling of blood that occurs within the brain tissue. A contusion is bruising in the brain—in a contusion, a bruise or an area of swelling can be seen on a CT scan but blood does not pool. The force of an impact on one side of the brain can cause the brain to bounce or ricochet within the skull. This can cause harm in two places—one directly beneath the 'hit', and a second area of damage on the opposite side of the brain.
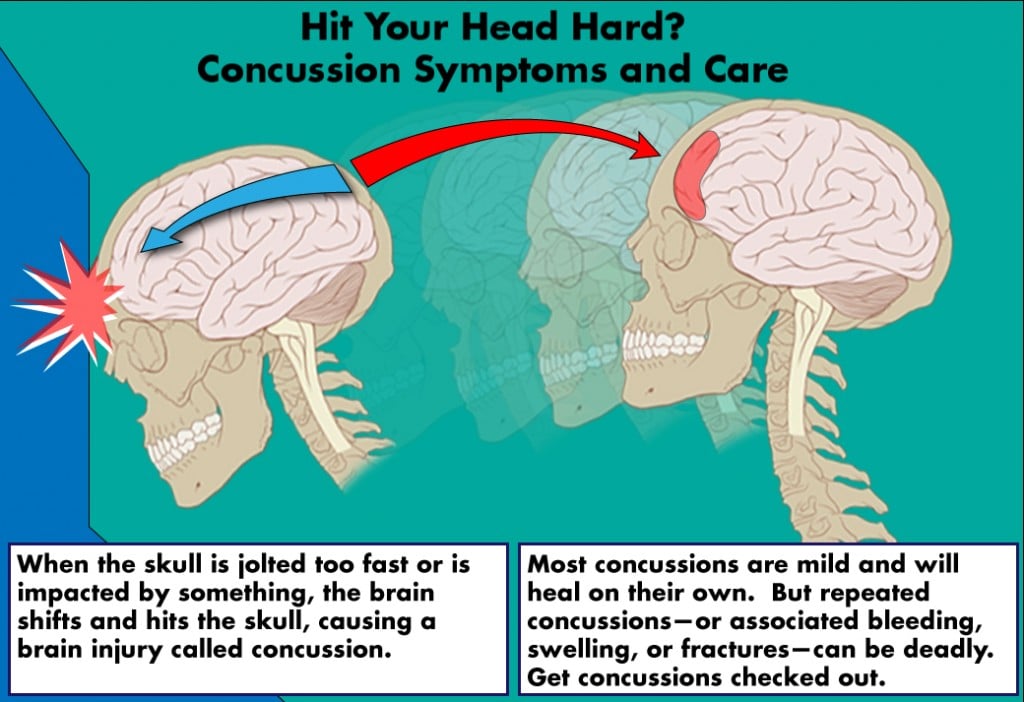
Concussion — If there are any symptoms of confusion, memory impairment or loss of consciousness after traumatic brain injury, the injury is called a 'concussion.' Symptoms of a concussion can include not having memory of the minutes immediately before the injury, temporarily losing consciousness, or having vomiting, dizziness, coordination problems, confusion, ringing in the ears, sleepiness or seizures. Head trauma can cause swelling inside the brain and a potentially deadly increase in pressure inside the skull.
Each year, head injuries result in more than 2 million emergency department visits in the United States, with more than 72,000 deaths. An additional 80,000 to 210,000 people with moderate or severe head injuries become disabled or require extended hospital care.
Overall, traumatic head injuries are the most common cause of death among Americans aged 45 and younger. In addition, head injuries resulting from falls are a very common cause of hospitalization and death among people older than 65. The US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reported that more than 25,000 adults over age 65 died in a recent year (2013) as a result of a fall—and many of these deaths were the result of head injuries.
Men are three to four times more likely than women to sustain head injuries, and alcohol use is involved in about 50% of cases.
In the United States, the most common causes of head injuries are motor vehicle accidents, falls and violent assaults.
Traumatic brain injury can also be caused by exposure to blast explosives in military combat, even if there is no direct contact with shrapnel. This is sometimes called 'shell shock.' Explosions cause a wave of changed atmospheric pressure, and brain movement within the skull can occur as a soldier recoils from a blast.
Up to 75% of people with severe head injuries also suffer serious damage to the neck bones or other parts of the body during the same injury.
Symptoms
Head injuries can cause a wide variety of symptoms, depending on the type of injury, its severity and its location. Some doctors classify head injuries into three categories, based on symptoms:
Mild head injury — There is minimal injury to the outside of the head, with no loss of consciousness. The injured person may vomit once or twice and complain of a headache.
Moderate head injury — There is a more obvious injury to the outside of the head, and the person may have lost consciousness briefly. Other symptoms can include memory loss (amnesia), headache, dizziness, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, confusion, a bruise-like discoloration around the eyes or behind the ear, or a clear fluid oozing from the nose. This fluid is not mucus, but fluid from around the brain (cerebrospinal fluid) that has leaked through a skull fracture near the nose.
Severe head injury — There is serious damage to the outside of the head, often together with injuries involving the neck, arms or legs or major body organs. In most cases, the person is either unconscious or barely responsive. However, some people become agitated or physically aggressive. About 10% of people with severe head injury have seizures.
Diagnosis
All head injuries should be evaluated promptly by a doctor, so either call for emergency help or have a friend or family member drive you to an emergency department. Once you arrive at the emergency department, the doctor will want to know:
How you hurt your head, including the height of your fall or your position (front seat, back seat, driver) in a car accident
Your immediate reaction to the injury, especially any loss of consciousness or memory loss. If you are with a person who has a head injury on a sports field, ask the player if he or she remembers the play that happened right before the injury. If memory is not perfect, this injury should be counted as a concussion, even if the person did not lose consciousness.
Any symptoms that occurred soon after the injury, such as vomiting, headache, confusion, sleepiness or seizures
Your current medications, including nonprescription drugs
Your past medical history, especially any neurological problems (stroke, epilepsy, etc.), any prior episodes of head injury, and your recent alcohol use if you are a heavy drinker
Whether you are having pain in your neck, chest, abdomen, arms or legs
If you are not able to answer these questions, the information can be provided by a family member, friend or the emergency medical personnel who brought you to the hospital.
The doctor will do a physical and neurological examination, including assessments of your pupil size, reflexes, sensation and muscle strength. If the results of these exams are normal, you may not need further tests. However, the doctor may decide to monitor your condition in the hospital.
If you have more severe head injuries, emergency personnel will try to stabilize your condition as much as possible before arrival at the hospital. To do this, they may pass a tube down your throat and windpipe (trachea) to help breathing with a mechanical ventilator, control any bleeding from open wounds, give medication intravenously (injected into a vein) to maintain blood pressure, and immobilize the person's neck in case of a cervical fracture.
Once you arrive at the hospital and are stabilized, the doctor will do a brief physical and neurological evaluation. This will be followed by a computed tomography (CT) scan of the head and spinal X-rays, if necessary. In most cases, a CT scan is the best way to detect skull fractures, brain injury or bleeding inside the head.
Expected Duration
Even if your head injury is only mild, you may have difficulty concentrating temporarily and may experience occasional headaches, dizziness and fatigue. This collection of symptoms is caused by a concussion. When symptoms are long-lasting, they are called 'post-concussion syndrome.' A concussion usually improves within three months.
You should not play contact sports until you have healed fully from a concussion. This can take weeks. The American Academy of Neurology has issued guidelines on the timing of an athlete's return to play. These guidelines recommend at least one week's rest after all concussion symptoms have gone away.
Computerized tests have been developed to identify subtle persisting symptoms of poor concentration, memory and coordination in athletes who have had concussions from head injuries. These tests can guide the timing of safe return to play.
The goal is to prevent two serious problems – repeat concussion and brain hemorrhage. Both of these are more likely to occur if the brain is still recovering from a first concussion.
A severe head injury can be fatal, or can require an extended hospital stay with prolonged rehabilitation. According to one large study, the average length of stay in a rehabilitation facility after severe head injury was 61 days. In some cases, disability is permanent.
Prevention
To help prevent head injuries, try the following suggestions:
If you drink alcohol, drink in moderation. Never drink and drive.
Wear a seat belt or helmet.
If you play sports, wear appropriate protective headgear.
If your job involves working high above the ground, use approved safety equipment to prevent accidental falls. Never work in a high place if you feel dizzy or light-headed, have been drinking alcohol, or are taking medication that can make you dizzy or affect your balance.
Have your vision checked at least once a year. Poor vision can increase your risk of falls and other types of accidents. This is especially true if you are elderly or if you work in high places.
Treatment
If you have minor head trauma, your doctor may decide to monitor your condition in the emergency department for a short period of time or to admit you to the hospital for a brief period of observation. While you are in the emergency department or in a hospital room, medical personnel will ask you periodically about your symptoms, check your vital signs and confirm that you are awake and can respond.
Once your doctor is satisfied that you can be sent home safely, he or she will allow you to leave on the condition that a responsible adult will stay with you at home for a day or two to help monitor your condition. This person will be given specific instructions about possible danger signs to watch for.
If you are troubled by headaches after your head injury, your doctor may suggest that you try acetaminophen (Tylenol) first. If this does not work, your doctor probably will prescribe a stronger pain reliever. Avoid taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Naprosyn) or indomethacin (Indocin) during your recovery period since these drugs can increase the risk of bleeding inside the head.
In people with more extensive head injuries, treatment depends on the type of injury, its severity and its location. In many cases, treatment takes place in an intensive care unit with mechanical ventilation (breathing assistance) and with medications to control pain, decrease swelling inside the brain, maintain blood pressure and prevent seizures. Surgery may be performed to repair a depressed skull fracture, drain an epidural or subdural hematoma or treat a brain hemorrhage or contusion.
The drug amantadine has been found to speed recovery of brain function after severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). The way this drug helps is not fully known, but it can change the mix of brain hormones in a way that might help recovery. In studies, hospitalized patients with TBI who received amantadine improved faster.
When To Call a Professional
Call for emergency help immediately if you find someone unconscious at an accident scene. Also call for emergency help if someone with a serious head injury experiences any of the following symptoms:
Headache
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Nausea and vomiting
Confusion
Difficulty walking
Slurred speech
Memory loss
Poor coordination
Irrational behavior
Aggressive behavior
Seizures
Numbness or paralysis in any part of the body
Even if your head injury appears to be less severe, and your symptoms are mild, it may be possible that you have had significant damage to the brain or its surrounding structures. This is especially true if you:
Are elderly
Take medication to thin the blood
Have a bleeding disorder
Have a history of heavy alcohol use
If you have one or more of the risk factors listed above, call a doctor or go to an emergency department immediately if you have a head injury.
Prognosis
The outlook depends on the severity of the injury:
Mild head injuries — The prognosis is usually very good. Although some people experience post-concussion syndrome, this typically goes away after about three months. In most cases, there is no long-term damage, although improvement may be gradual.
Moderate head injuries — The most dramatic improvement usually occurs within the first one to six weeks. After that time, there may be some remaining problems with memory or attention, but these may not be permanent.
Severe head injuries — Up to 50% of severe head injuries are fatal. Among people who survive these injuries, about 20% suffer severe disabilities.
External resources
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
P.O. Box 5801
Bethesda, MD 20824
Phone: 301-496-5751
Toll-Free: 1-800-352-9424
TTY: 301-468-5981
http://www.ninds.nih.gov/
American Academy of Neurology (AAN)
1080 Montreal Ave.
St. Paul, MN 55116
Phone: 651-695-2717
Toll-Free: 1-800-879-1960
Fax: 651-695-2791
http://www.thebrainmatters.org/
Family Caregiver Alliance
180 Montgomery St.
Suite 1100
San Francisco, CA 94104
Phone: 415-434-3388
Toll-Free: 1-800-445-8106
Fax: 415-434-3508
http://www.caregiver.org/
Sleeping After Hitting Your Head
National Rehabilitation Information Center (NARIC)
4200 Forbes Blvd.
Suite 202
Lanham, MD 20706
Phone: 301-459-5900
Toll-Free: 1-800-346-2742
TTY: 301-459-5984
http://www.naric.com/
Brain Injury Association of America
8201 Greensboro Drive
Suite 611
McLean, VA 22102
Phone: 703-761-0750
Toll-Free: 1-800-444-6443
Fax: 703-761-0755
http://www.biausa.org/
Brain Trauma Foundation
523 E. 72nd St.
New York, NY 10021
Phone: 212-772-0608
Fax: 212-772-0357
http://www.braintrauma.org/
National Institute on Disability and Rehabilitation Research
400 Maryland Ave., S.W.
Washington, DC 20202-7100
Phone: 202-245-7640
TTY: 202-245-7316
http://www.ed.gov/about/offices/list/osers/nidrr/index.html?src=mr/
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
U.S. Department of Transportation
400 7th St., SW
Washington, DC 20590
Toll-Free: 1-888-327-4236
http://www.nhtsa.dot.gov/
U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)
4330 East-West Highway
Bethesda, MD 20814-4408
Phone: 301-424-6421
Toll-Free: 1-800-638-2772
Fax: 301-413-7107
http://www.cpsc.gov/
Symptoms Of Hitting Your Head Brain Dmg Download
Further information
Symptoms Of Hitting Your Head Brain Dmg 2
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.